Fuels
Treating sludge onboard
17 February 2026
Please note this article was published in November 2016 and the facts and opinions expressed may no longer be valid.
09 November 2016
New insights on winter diesel fuel quality

The 2016 Infineum Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey provides an analysis of diesel fuels collected from around the world. Insight reveals the key trends and highlights the wide variations in fuel quality that still exist from country to country.
The 2016 Infineum Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey (WDFQS) provides a snapshot of the quality of diesel fuel collected in the deep winter months from retail stations around the world. The most interesting trends this year include the changing use of renewable fuels, sulphur levels and lubricity performance.
Samples were collected from 50 countries and analysed for a number of parameters, the full data set is presented in the Survey results here.

On a global level in the 2016 WDFQS, a higher percentage of samples contained no fatty acid methyl ester (FAME) (B0) than in 2014. In addition, where FAME is used, a lower percentage of samples had FAME levels over B5.
FAME use across the globe is driven by mandates and/or subsidies, and refiners select the most cost competitive solution to meet blend targets. However, quality concerns and operability issues may be driving the market away from FAME use, particularly in the winter months where quality may be more of a concern.

However, the trends in the use of FAME vary widely on a regional basis and are generally driven by local mandates, incentives, cost and availability.

Governments around the world are introducing or increasing renewable fuels blend targets. However, the term 'renewable' covers a wide range of sources and, as regulations and incentives for the use of FAME change, refiners may use alternatives.
This year’s survey shows the first definite signs of hydrogenated vegetable oil (HVO) used as a renewable diesel fuel in Europe (particularly in Sweden and Spain) and also in the US.

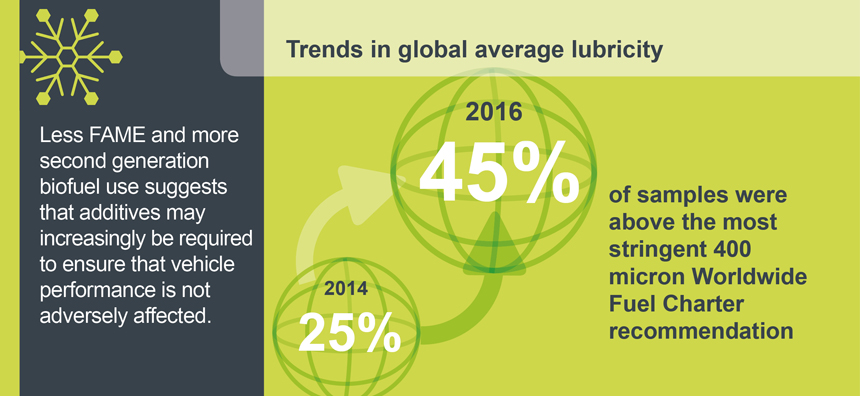
Global average wear scar diameter, which had been decreasing in previous surveys, now remains stable, or is slightly increasing globally.
Lubricity additives may increasingly be required to ensure that vehicle performance is not adversely affected.
In Europe and North America very low sulphur limits for diesel fuels have been in place for some years.
However, in those countries that are still working towards the ‘ultra low sulphur diesel’ benchmark, there has been a continued downward trend in diesel fuel sulphur levels.

In particular, this Survey highlights a huge drop in sulphur in some of the Middle Eastern countries compared to 2014, which is being driven by both internal requirements and the growing export of refined products.
All of these winter diesel fuel quality trends mean expert advice on specification requirements and the use of proven additive technology are increasingly important to help fuel producers address the growing list of challenges facing the industry.
Read the full report and view the data from the 2016 WDFQS here.
Fuels Technologists from Infineum have been tracking the trends in diesel fuel quality in this biennial survey for many years, providing the industry with a comprehensive picture of the global changes.
Read the introduction and trends from previous WDFQS:
If you have any questions or comments about the Infineum Winter Diesel Fuel Quality Survey please contact the Infineum Fuels Team.
Sign up to receive monthly updates via email
